Simplify Your Editing Process: Remove Object from Photo
Introduction In the realm of photography, editing plays a crucial role in enhancing the visual appeal of images. Whether you’re a professional photographer or an…

Introduction In the realm of photography, editing plays a crucial role in enhancing the visual appeal of images. Whether you’re a professional photographer or an…

In the realm of interior design, lighting plays a pivotal role in setting the mood and ambiance of a space. A well-designed living room requires…

Microsoft SQL Server and PostgreSQL are both extremely popular RDBMS having rich set of administration tools and programming APIs. However, MS SQL has quite restrictive…

It has been over six months since ChatGPT emerged and impressed the entire world. People expected companies to develop Artificial Intelligence to conduct daily routine…

Hulu is widely recognized as a popular streaming platform that offers a diverse selection of TV shows, movies, and exclusive content. It is primarily accessible…

24/7 Monitoring and Response When you outsource SOC, you will get continuous monitoring of your cybersecurity. This helps to reduce the risk of incidents since…

Creating or designing a landing page that effectively converts visitors into customers is a critical component of digital marketing and online business success. A well-crafted…
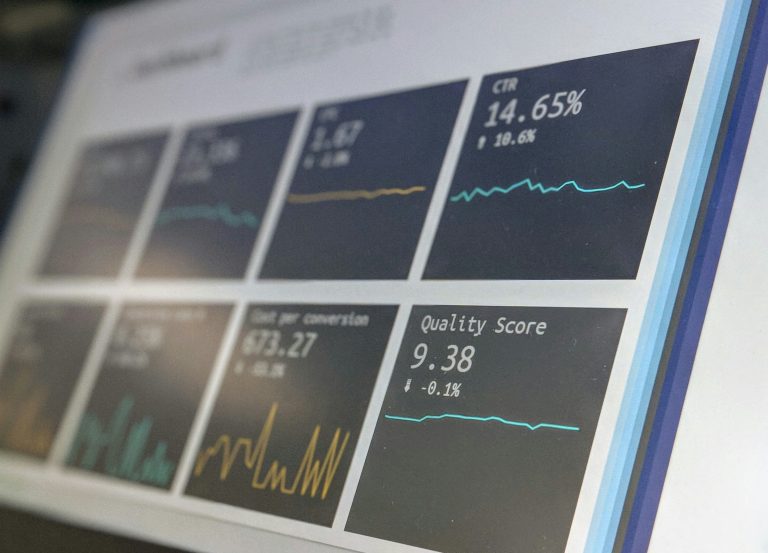
In the ever-evolving landscape of search engine optimization (SEO), staying ahead of the curve is essential for achieving and maintaining high search engine rankings. One…

The way businesses relate to each other, stakeholders, customers, and employees paints a deeper picture of the corporate world and underscores the vital role of…

There are certain factors that are frequently unavoidable in conveyor designs, mainly when working in confined spaces or avoiding manufacturing supports and installed equipment. Numerous…

Bitcoin (BTC) was initially designed to function as mobile money. Anonymous creator Satoshi Nakamoto described the asset in the 2008 whitepaper as a peer-to-peer cash…

Introduction Is the daunting task of cleaning your staircase leaving you in a dizzy spell? Surprisingly, stairs are dubbed some of the hardest areas to vacuum. We’ll help…

In today’s bustling digital marketplace, the spotlight shines brightly on how we can transact online not just with ease but with unwavering security. As we…

Are you planning to venture into the e-commerce world? Well, that’s good news. Now is the right time to enter the field. We say so…

In the age of rapid technological advancement, Artificial Intelligence (AI) stands as the most pertinent concept and a hot topic of conversation across the globe,…